Bevezetés
In the realm of industrial manufacturing, precision and efficiency are paramount. One technology that has significantly transformed the landscape is the big laser cutter. These powerful machines have become indispensable in various industries, from automotive to aerospace, due to their ability to cut through a wide range of materials with unparalleled accuracy. This article delves into the intricacies of big laser cutters, exploring their functionality, benefits, applications, and the future of this cutting-edge technology.
What is a Big Laser Cutter?
A big laser cutter is a high-powered machine that uses a laser beam to cut materials with extreme precision. These machines are typically larger in size compared to their smaller counterparts, allowing them to handle bigger workpieces and more complex designs. The laser beam is generated by a laser source, usually a CO2 or fiber laser, and is directed onto the material through a series of mirrors and lenses. The intense heat generated by the laser beam melts, burns, or vaporizes the material, resulting in a clean and precise cut.
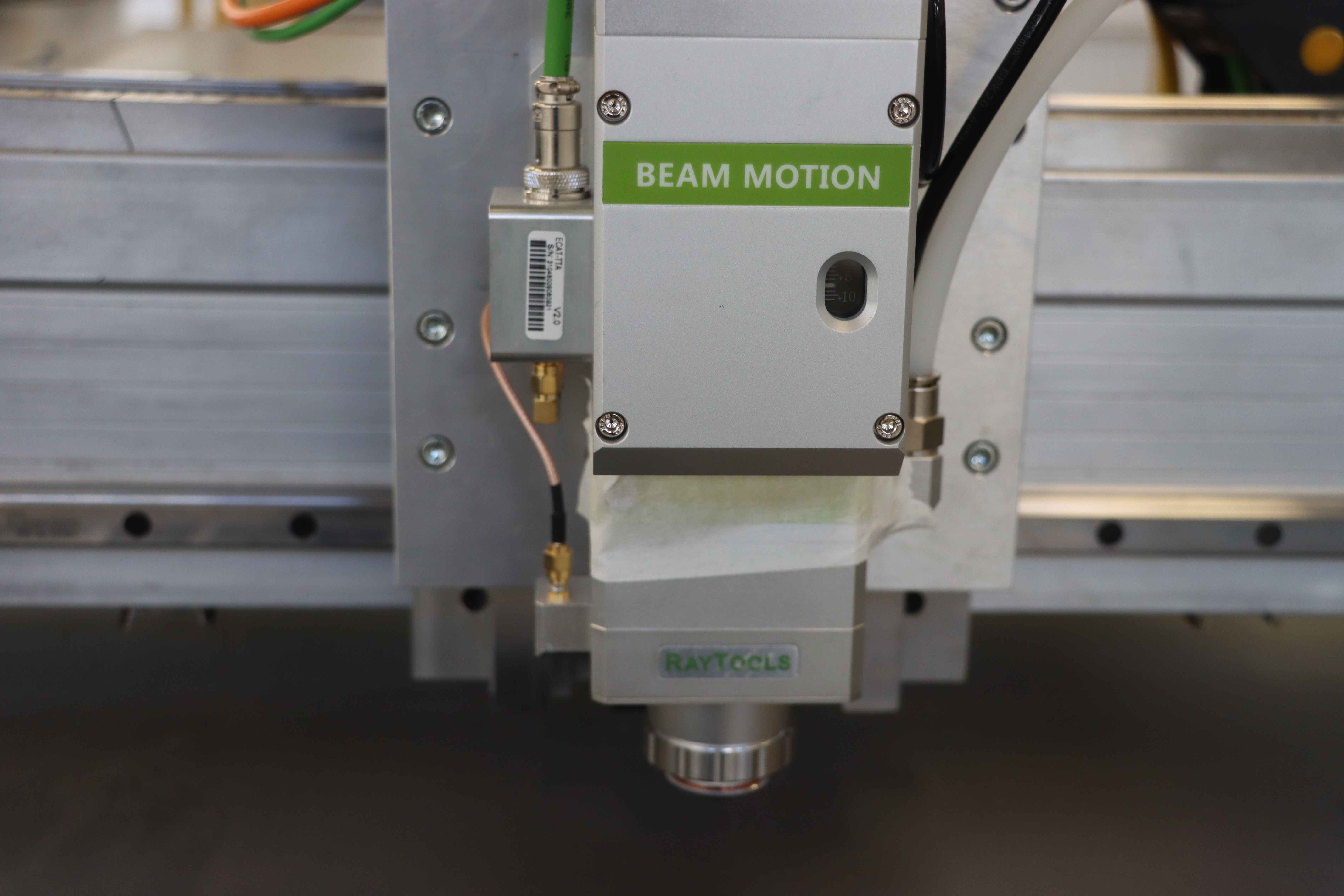
Types of Big Laser Cutters

1. CO2 Laser Cutters These are the most common type of big laser cutters, known for their versatility and ability to cut through a wide range of materials, including wood, acrylic, glass, and certain metals. CO2 lasers are highly efficient and produce a high-quality finish, making them ideal for industrial applications.
2. Fiber Laser Cutters Fiber laser cutters are renowned for their ability to cut through metals with exceptional precision. They use a fiber optic cable to generate the laser beam, which is then focused onto the material. Fiber lasers are highly energy-efficient and offer faster cutting speeds compared to CO2 lasers, making them the preferred choice for metal cutting applications.
3. NdYAG Laser Cutters These laser cutters use a neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet crystal to generate the laser beam. NdYAG lasers are capable of cutting through thick metals and are often used in heavy-duty industrial applications. However, they are less common than CO2 and fiber lasers due to their higher cost and maintenance requirements.
Key Components of a Big Laser Cutter
1. Laser Source The heart of the laser cutter, the laser source generates the high-powered laser beam used for cutting. The type of laser source (CO2, fiber, or NdYAG) determines the machine's capabilities and the materials it can cut.
2. Cutting Bed The cutting bed is the surface on which the material to be cut is placed. Big laser cutters typically have large cutting beds to accommodate bigger workpieces. The bed may be stationary or movable, depending on the machine's design.
3. Control Panel The control panel is the interface through which the operator controls the laser cutter. It allows the operator to set cutting parameters, such as laser power, cutting speed, and focus, and to monitor the cutting process.
4. Cooling System Laser cutters generate a significant amount of heat during operation, which can affect the machine's performance and longevity. A cooling system, usually a water chiller, is used to dissipate this heat and maintain the laser cutter's optimal operating temperature.
5. Exhaust System The cutting process produces fumes and debris, which need to be removed to maintain a clean working environment and prevent damage to the machine. An exhaust system, often equipped with a fume extractor, is used to remove these byproducts.
Advantages of Big Laser Cutters
1. Precision and Accuracy Big laser cutters offer unparalleled precision and accuracy, allowing for intricate and complex designs to be cut with ease. The laser beam's fine focus ensures clean and sharp edges, reducing the need for post-processing.
2. Versatility These machines can cut a wide range of materials, from metals and plastics to wood and glass. This versatility makes them suitable for various industries and applications.
3. Speed and Efficiency Big laser cutters are capable of cutting at high speeds, significantly reducing production time. Their efficiency also translates to cost savings, as less material is wasted during the cutting process.
4. Automation and Integration Many big laser cutters are equipped with advanced automation features, such as CNC (Computer Numerical Control) systems, which allow for precise control and repeatability. They can also be integrated into larger production lines, further enhancing efficiency.
5. Minimal Maintenance Compared to traditional cutting methods, big laser cutters require minimal maintenance. The absence of physical cutting tools reduces wear and tear, and the machines are designed for long-term reliability.
Applications of Big Laser Cutters
1. Automotive Industry Big laser cutters are widely used in the automotive industry for cutting metal components, such as chassis, body panels, and engine parts. Their precision and speed make them ideal for high-volume production.
2. Aerospace Industry The aerospace industry demands high precision and quality, which big laser cutters can deliver. They are used to cut complex components for aircraft, such as turbine blades, fuselage sections, and structural elements.
3. Construction Industry In the construction industry, big laser cutters are used to cut metal beams, panels, and other structural components. Their ability to handle large workpieces makes them suitable for construction projects.
4. Electronics Industry The electronics industry relies on big laser cutters for cutting precise components, such as circuit boards, enclosures, and connectors. The clean cuts produced by laser cutters ensure the integrity of electronic components.
5. Art and Design Big laser cutters are also used in the art and design industry for creating intricate patterns, sculptures, and decorative elements. Their precision and versatility allow artists to bring their creative visions to life.
Future Trends in Big Laser Cutter Technology
1. Increased Automation The future of big laser cutters lies in increased automation. Advanced CNC systems and robotics will further enhance the precision and efficiency of these machines, reducing the need for manual intervention.
2. Integration with AI and IoT The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) will enable big laser cutters to operate more intelligently. AI algorithms can optimize cutting parameters in real-time, while IoT connectivity allows for remote monitoring and control.
3. Enhanced Material Compatibility Future big laser cutters will be capable of cutting an even wider range of materials, including advanced composites and ceramics. This will expand their applications in industries such as aerospace and electronics.
4. Energy Efficiency As sustainability becomes a priority, big laser cutters will be designed to be more energy-efficient. Advances in laser technology and cooling systems will reduce energy consumption, making these machines more environmentally friendly.
5. Compact and Modular Designs While big laser cutters are known for their size, future models may feature more compact and modular designs. This will make them more versatile and easier to integrate into existing production lines.
Conclusion
Big laser cutters have revolutionized industrial manufacturing, offering precision, speed, and versatility that traditional cutting methods cannot match. From automotive to aerospace, these machines have become essential tools in various industries. As technology continues to advance, big laser cutters will become even more powerful, efficient, and intelligent, further enhancing their capabilities and applications. Whether you're in manufacturing, construction, or design, investing in a big laser cutter can significantly boost your productivity and quality, ensuring you stay ahead in the competitive industrial landscape.
Függetlenül attól, hogy általános tanácsra vagy konkrét támogatásra van szüksége, örömmel segítünk Önnek.